Freedom of Navigation Monitoring
- All
- Russian Blood-Soaked Export
- Crimea Under Occupation
- Militarization of the Black Sea
- Freedom of Navigation Monitoring
- Sanctions
- Crimea Before Occupation
- Pre-War Archive

The grain corridor in the Black Sea in June – July 2023: The final statistics and database
02 August 2023
Long periods, starting from 9 May 2023, when no ships arrived at the ports, were explained not by weather conditions, but solely by the blocking of inspections by Russian JCC inspectors under various pretexts.
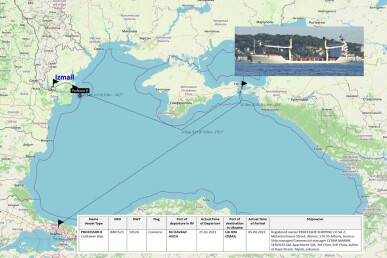
Foreign Merchant Ships Calling at Russian Ports Before Proceeding to the Ukrainian Ones
01 July 2023
Initially, a direct voyage from a Russian port to a Ukrainian one during the war struck us as a coincidence that, however, prompted us to start checking for similar voyages by other vessels. As a result, we've easily identified a fairly significant number of vessels that arrived at Ukrainian ports having previously called at the Russian ports. For security reasons, including counteracting possible sabotage, special decisions should be made to prevent maritime businesses from chartering vessels that operate to Russian ports for the transportation of goods to/from Ukrainian ports or simply ban such vessels from entering Ukrainian ports.
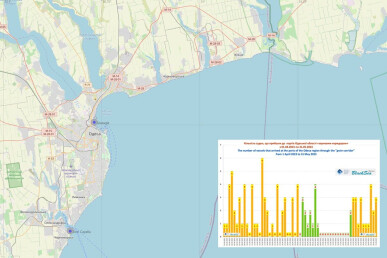
The grain corridor in the Black Sea in April-May 2023: Russia’s ultimatum demanding the lifting of sanctions
31 May 2023
No ships arrived at Ukrainian ports through the grain corridor from 9 to 20 May 2023. There have been no interruptions for such a long time since the beginning of the Black Sea Grain Initiative. This happened soon after 13 April 2023, when Russia for the first time formally compiled a detailed list of demands for the lifting of sanctions in return for its further participation in the Grain Initiative. The demands were presented in the form of an ultimatum to the UN Secretariat, although the UN cannot resolve the issue of easing sanctions.
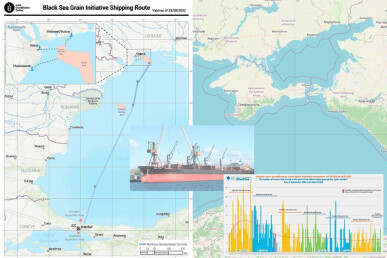
The Black Sea «Grain Corridor» between September 2022 - March 2023 — New Highlights
17 March 2023
The average daily number of ships arriving at the ports of Odesa as part of the «Black Sea Grain Initiative» is one of the indicators of military risks for the region. While in September 2022, it averaged 5.9 vessels per day, in October – 5.1, in November 2022 – 3.3, in December – 3.2, in January 2023 – 2.8, in February – 2.5 and between March 1-10, 2023 – 2.8 vessels per day. The decrease is the result of Russia conscious policy of inspecting no more than 3-4 vessels per day as part of its joint inspections with Turkey. The RF agreement to extend the «grain initiative» for 60, instead of the previous 120 days, is predetermined by the single factor — the May 14, 2023 presidential and parliamentary elections in Turkey.

The "grain corridor" in the Black Sea in September-December 2022. Important statistics
22 January 2023
The average number of vessels arriving per day at the ports of Odesa as part of the Black Sea Grain Initiative is one of the indicators of military risks. In September 2022, it was 5.9 vessels per day; in October – 5.1; in November – 3.3; and in December – 3.2. That is, in November, as a result of Russia’s deliberate actions, the number of vessels receiving permits for voyages to Ukrainian ports almost halved. Blocking the "grain corridor" remains an integral part of Putin's plan for a new stage of the war. That is, in the event of a new Russian offensive, the "grain corridor" may be blocked.
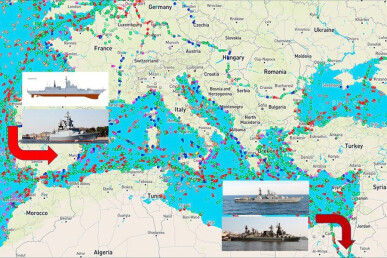
The presence of Russian warships in the Mediterranean Sea as of 6 November 2022
06 November 2022
As we have predicted earlier, Russia continues the reduction and rotation of its naval group in the Mediterranean. On 16 October 2022, 2 missile corvettes of the Russian Baltic Fleet - (531) Soobrazitelnyi and (545) Stoikiy - entered the Mediterranean Sea through the Strait of Gibraltar. On 21 October 2022, the missile cruiser (011) Varyag, the flagship of the Pacific Fleet of the Russian Federation (PF), the large anti-submarine ship (564) Admiral Tributs (PF), and the oil tanker/supply ship Boris Butoma left the Mediterranean Sea through the Suez Canal.
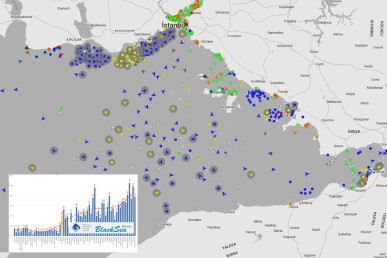
The “grain corridor”: Russia has artificially increased the waiting time for the inspection of ships carrying Ukrainian grain in the Sea of Marmara
01 November 2022
Since 18 September 2022, the waiting time for the “grain fleet” vessels to be inspected by the Joint Coordination Centre (JCC) in the Sea of Marmara has increased by 5 times and reached 11.3 days per vessel. Such a situation is totally disadvantageous for 3 out of 4 participants of the "grain initiative" - the UN, Turkey, and Ukraine. Our main assumption is that Russia is once again using this situation in connection with other issues - for example, the ceasefire on the front line, which is located at a distance of 40-60 km from the grain corridor area.

The Presence of Russian Warships in the Mediterranean Sea as of 10 October 2022
12 October 2022
As of October 10, 2022, the confirmed composition of the Russian Navy ship group in the Mediterranean Sea includes 8 warships — 6 of which missile — and 3 auxiliary vessels. On September 19, 2022, the Baltic Fleet reconnaissance ship Vasiliy Tatishchev left the Mediterranean Sea via Gibraltar and on September 24, 2022, — the Black Sea Fleet missile submarine Novorossiysk accompanied by the Sergey Balk tug. We maintain that the Russian Navy will continue this Mediterranean Sea rotation in the near future.
As of September 26, 2022, 60 of 100 vessels remain blocked in the ports of Ukraine/ Database
28 September 2022
As of February 24, 2022, 100 commercial vessels docked in the Ukrainian ports, not counting those of the occupied Crimea, all of which remained under the naval blockade by the Russian Federation. Of these 100, 34 belong to ship-owning companies from the EU countries, namely, 21— Greece and 24 — Turkey. As of September 26, 60 of the 100 vessels remain blocked: 29 – in the Mykolaiv region ports, 14 – in Kherson and 5 – in Mariupol. For various reasons, 12 of the 41 that were blocked on February 24, currently remain in the ports of the Odesa region.
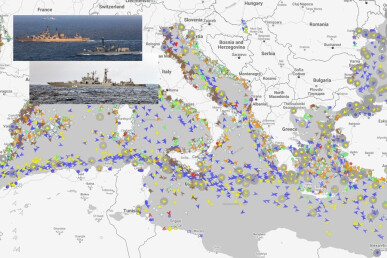
The Presence of Russian Warships in the Mediterranean Sea as of 15 September 2022
16 September 2022
In late summer of 2022, Russia began the rotation of part of its warships in the Mediterranean Sea. missile ships of the Northern Fleet, a reconnaissance ship of the Black Sea Fleet, 2 oil tankers of the Black Sea and Northern Fleets were withdrawn from the Mediterranean Sea. As of 15 September 2022, the confirmed composition of the Russian Navy squadron in the Mediterranean Sea includes 10 ships (7 of which are missile ships) and 4 auxiliary vessels. If another missile submarine is officially confirmed to be in the Mediterranean, the total number of ships will change from 10 to 11, and the number of missile ships will rise from 7 to 8.
Blocked ships in Ukrainian ports during the war: The commercial sea port of Chornomorsk
31 July 2022
As of 24/02/2022, in the commercial sea port of Chornomorsk, in addition to port fleet vessels permanently based in Chornomorsk, there were 23 merchant ships. All of them have remained in port under blockade. Thus, out of 23 ships in the sea port of Chornomorsk, 6 belong to Turkish shipowners, 4 - to Ukrainian shipowners, 8 - to shipowners from the EU and the UK. Companies from Georgia, Japan, China, the UAE (in fact, Russia), and Liberia own one ship each.

Blocked ships in Ukrainian ports during the war: The Odesa commercial sea port
27 July 2022
As of 24/02/2022, in the Odesa commercial sea port, in addition to port fleet vessels permanently based in Odesa, there were 9 merchant ships. All of them have remained in port under sea blockade. So, out of 9 ships in the sea port of Odesa, 2 belong to Turkish shipowners, 6 - to shipowners from EU countries - Germany and Greece, and one ship is owned by a company from Liberia.

Blocked ships in Ukrainian ports during the war: The port of Kherson
24 June 2022
The Monitoring Group of the Black Sea Institute of Strategic Studies and BlackSeaNews wishes to bring to your attention a new series of articles about the fate of ships that were in Ukrainian ports on 24 February 2022, when Russia launched a full-scale invasion of many regions of Ukraine.
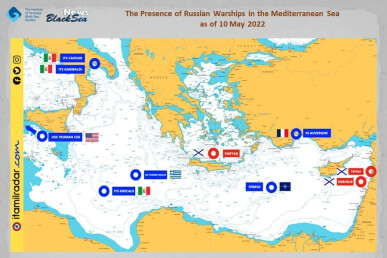
The Presence of Russian Warships in the Mediterranean Sea as of 10 May 2022
11 May 2022
As of 10 May 2022, the same naval group is present in the Mediterranean Sea as was on 7 February 2022 - i.e. no changes have taken place over the last 3 months. There are 13 ships and 5 support vessels of the four Russian fleets, including 9 attack missile ships. This situation is a consequence of Turkey’s decision, which was announced on 27 February 2022, to ban the passage through the straits of any warships, including ships of non-Black Sea NATO countries

Blocked ships in Ukrainian ports during the war: the Pivdenny commercial sea port
11 May 2022
As of 24 February 2022, in the Pivdennyi commercial sea port (Yuzhne city, the Odesa region, Ukraine, international port code UA YUZ), in addition to port fleet vessels permanently based in the port, there were 9 merchant ships (See Table 1). All of them have remained in port under blockade. Thus, out of the 9 ships blocked in the Pivdennyi sea port, 6 belong to shipowners from EU countries, 3 - to shipowners from Japan.